GHANA INVESTMENT
PROMOTION CENTRE FOCUS
Ghana’s infrastructure sector
Infrastructure remains a key development priority to sustain Ghana’s rapid urbanization and industrial growth as well as attainment of the post 2015 development agenda and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The national development framework therefore seeks to expand existing social and economic production infrastructure to ensure that services provided are reliable, affordable and efficient.
Whilst public investment in infrastructure has increased, the country is also actively engaged in involving the private sector to meet growing demand, through the Public Private Partnership (PPP) initiative. The policies of the Ghanaian Government seek to encourage investments in domestic infrastructure from both local and foreign private capital.
Focus on various sub-segments & allied services
HARD & SOFT INFRASTRUCTURE
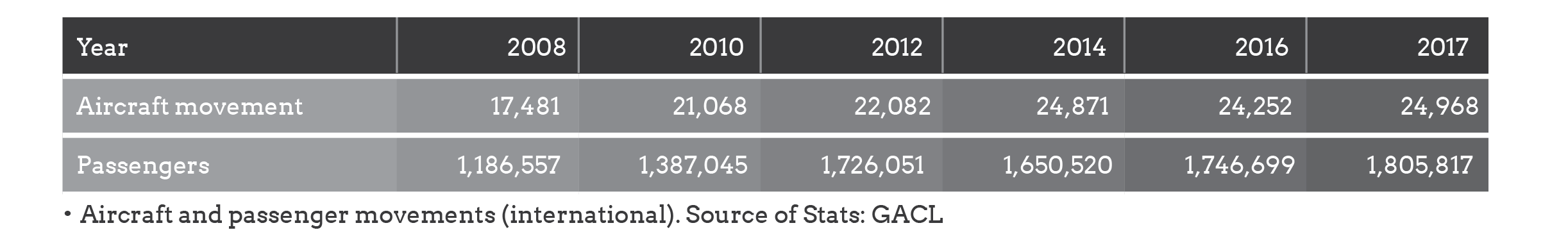
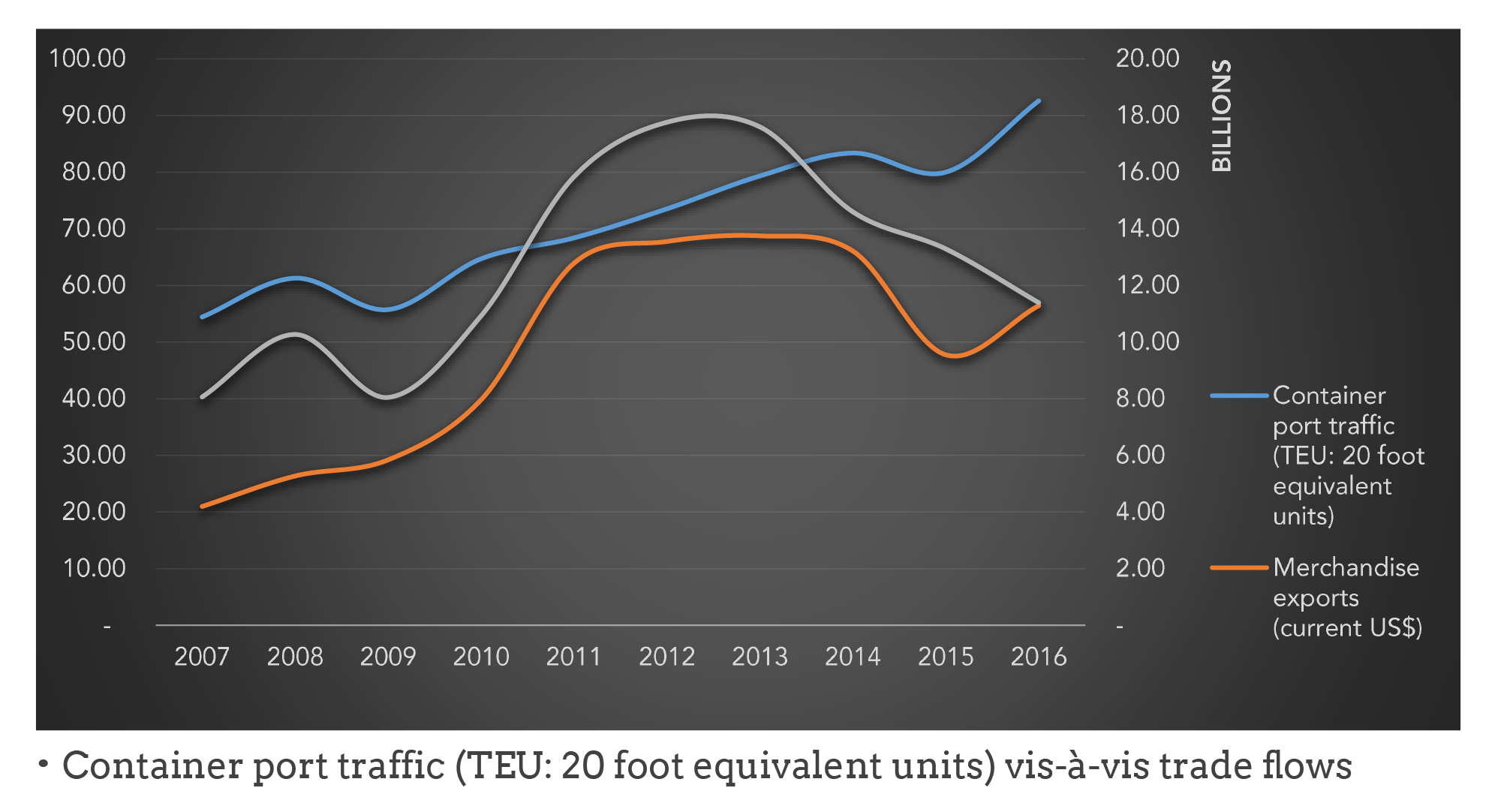
It is quite noteworthy that the soft components of Ghana’s infrastructure base (like telecom, air and port services) have witnessed improving performance over the past two decades, thereby helping the country to maintain satisfactory growth. For instance, the country’s rising trade has been reflected in growing container port traffic, which increased from a low of 544,294 in 2007 to about 925,964 in 2017. Correspondingly, certain hard components, like roads, have witnessed tremendous expansion over the last two decades. Performance in the railway sector has however been met with challenges, in terms of access or spread of rail length.
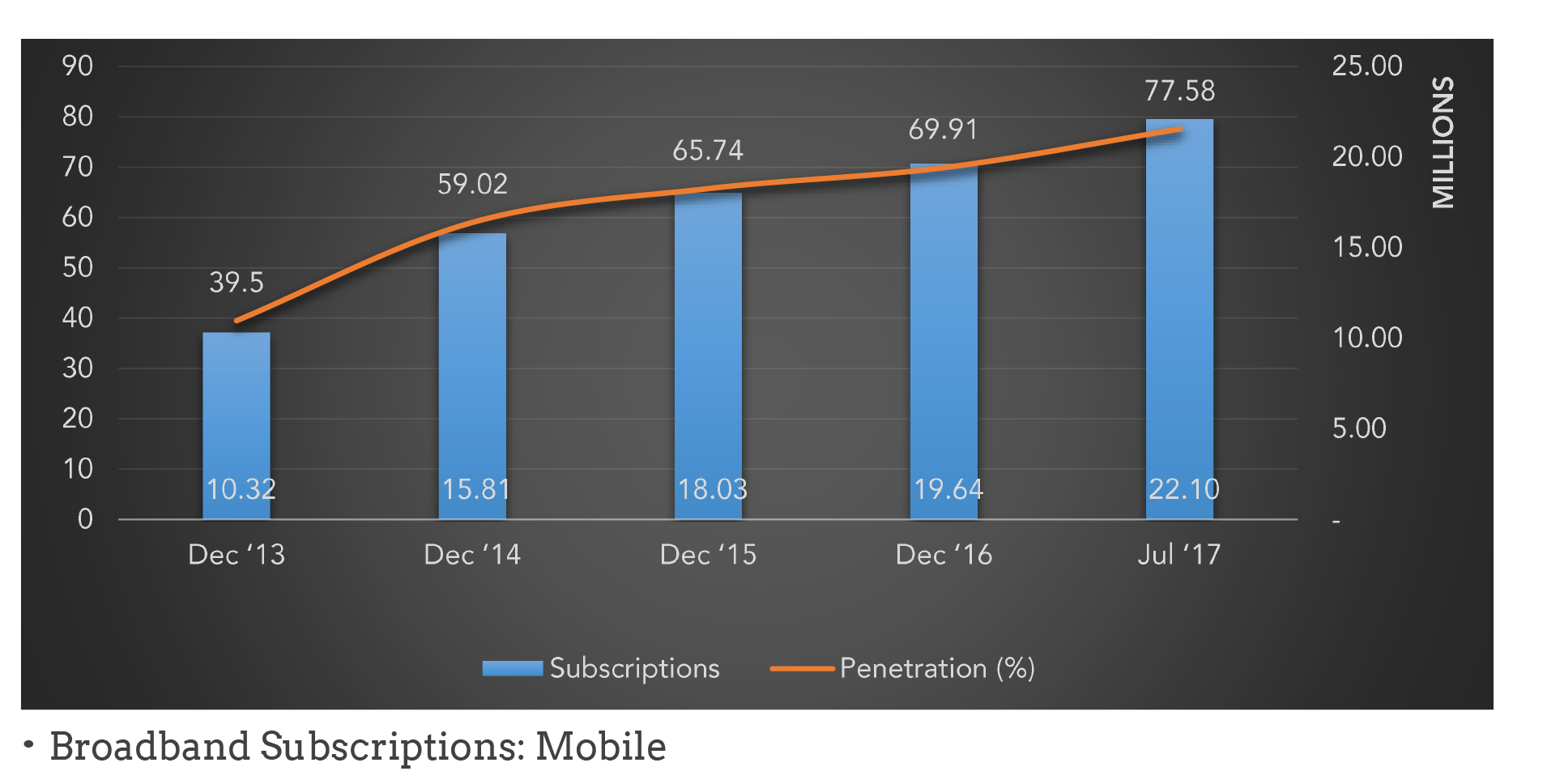
The figures highlight trends regarding some of the soft indicators.
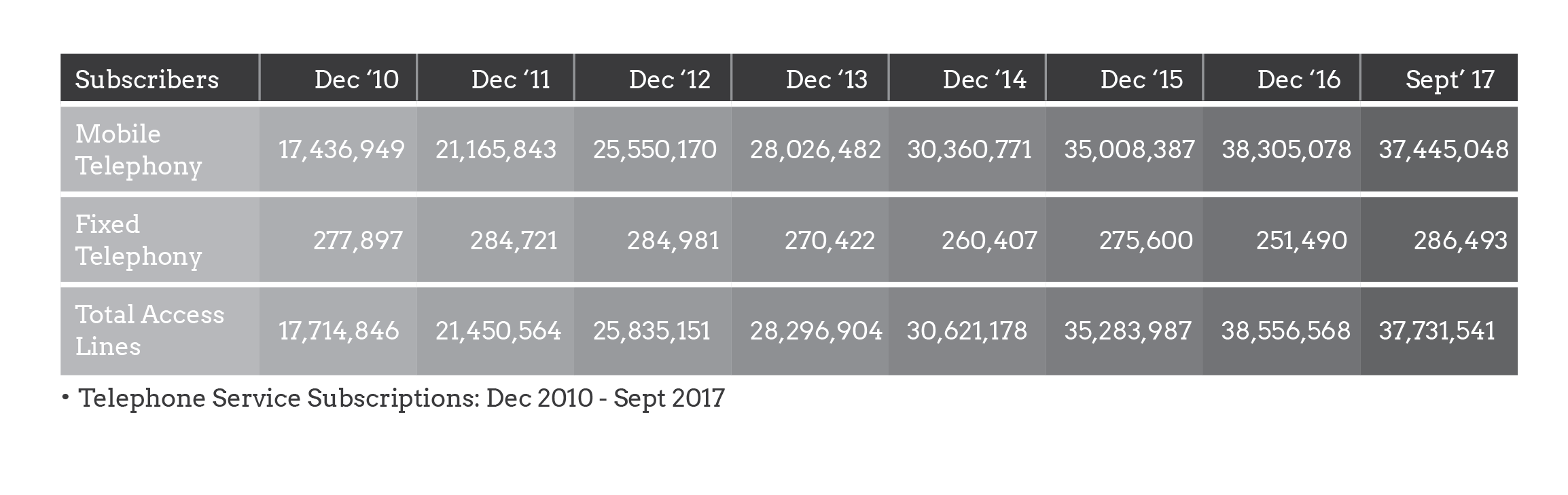
The subsequent sections throw more light on the various sub-sectors.
TRANSPORTATION
The Transport sub-sector is made up mainly of road transport, maritime and water transport, aviation and rail. The fundamental policy objective of the transport sector is to establish an efficient and modally complementary and integrated transport system. Therefore, Government encourages private sector engagement in this sector.
AVIATION
Ghana presently has one international airport- The Kotoka International Airport, located in the capital city Accra, which connects the country and the rest of the world. There are also five other domestic airports (located in Kumasi, Sunyani, Tamale, Ho and Takoradi) and two airstrips (located in Wa and Kpong). The country is in the advanced stages of establishing a new national airline. Despite this, Ghana is served by a number of airlines that connect international routes via Johannesburg, Cape Town, Addis Ababa, Nairobi, London, Amsterdam, Dubai and Dar-Es-Salaam etc. Major airlines operating in the country include Africa World Airlines, Ethiopian Airlines, South African Airways, KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, British Airways, Middle East Airlines (MEA), Kenya Airways, Alitalia, Royal Air Maroc, Lufthansa, Egyptair, etc. Government has embarked on a program to improve the infrastructure at the various airports including the expansion of the Kotoka International Airport and the upgrade of the Kumasi Airport and the Tamale Airports into international status.
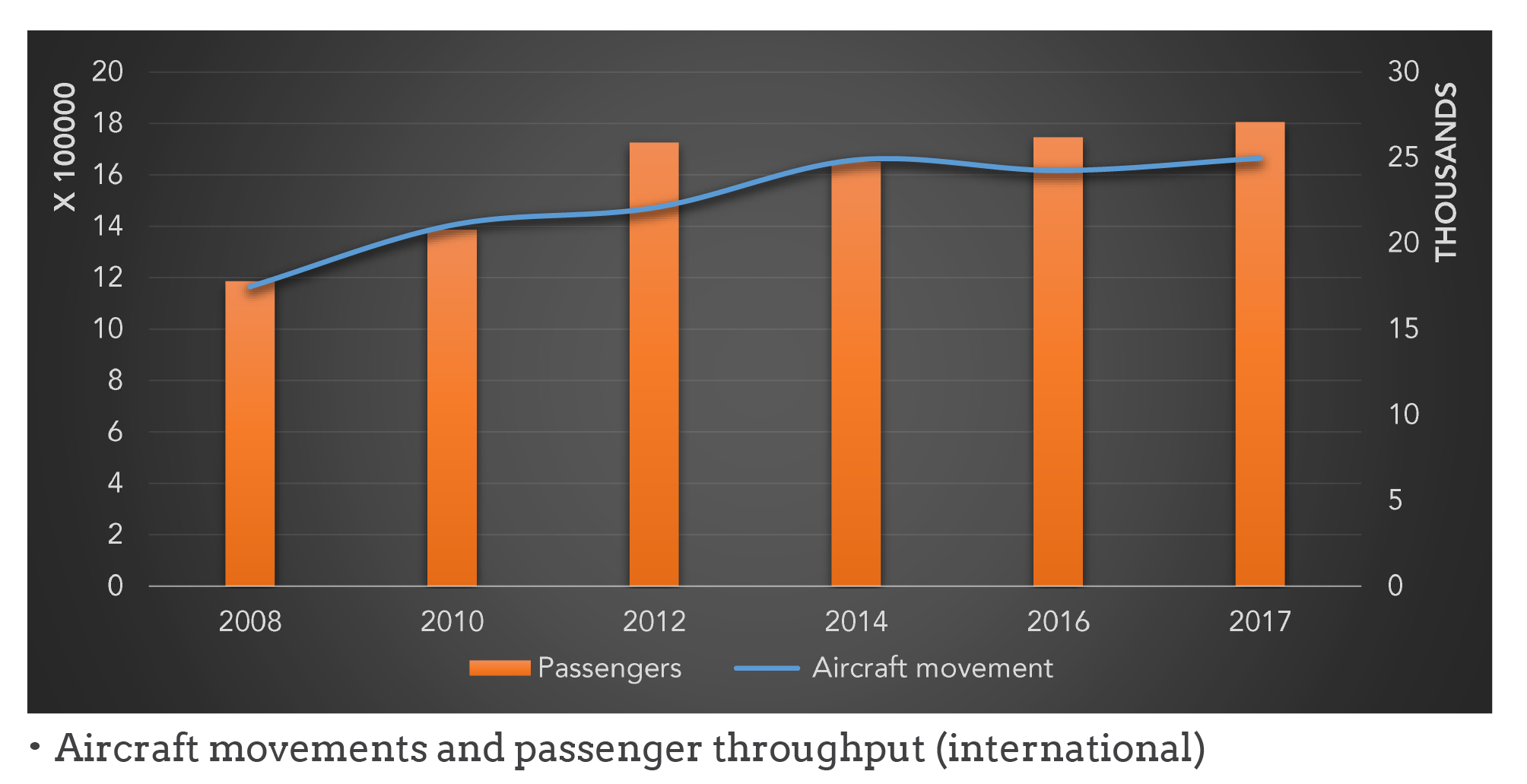
The chunk of Ghana’s air transport market is international and over the past few years, passenger numbers have grown massively in this regard. With improving income levels complemented with the location of foreign enterprises in the country, the air transport industry has good prospects. Relatively lower volumes in the domestic air transport sector also offers enormous future potential.
The figures below highlight trends in the sub-sector.